

 Location: Southern Asia, in the
Indian Ocean off the southwest coast of India
Location: Southern Asia, in the
Indian Ocean off the southwest coast of India
Map references:
Asia, Standard Time Zones of the World
Area:
total area 300 sq km
land area 300 sq km
comparative area
slightly more than 1.5 times the size of Washington, DC
Land boundaries: 0 km
Coastline: 644 km
Maritime claims:
exclusive economic zone 35-310 nm as defined
by geographic coordinates; segment of zone coincides with maritime boundary
with India
territorial sea 12 nm
International disputes:
none
Climate: tropical; hot, humid; dry, northeast
monsoon (November to March); rainy, southwest monsoon (June to August)
Terrain: flat with elevations only as high as 2.5 meters
Natural resources: fish
Land use:
arable land
10%
permanent crops 0%
meadows and pastures
3%
forest and woodland 3%
other 84%
Irrigated land: NA sq km
Environment:
current issues
depletion of freshwater aquifers threatens water supplies
natural hazards
low level of islands makes them very sensitive to sea level rise
international agreements party to - Biodiversity, Climate Change, Hazardous
Wastes, Ozone Layer Protection; signed, but not ratified - Law of the Sea
Note: 1,200 coral islands grouped into 19 atolls; archipelago
of strategic location astride and along major sea lanes in Indian Ocean
 Population: 252,077 (July 1994 est.)
Population: 252,077 (July 1994 est.)
Population growth rate: 3.61% (1994 est.)
Birth rate: 43.59 births/1,000 population (1994 est.)
Death rate: 7.45 deaths/1,000 population (1994 est.)
Net migration rate:
0 migrant(s)/1,000 population (1994 est.)
Infant mortality rate:
53.8 deaths/1,000 live births (1994 est.)
Life expectancy at birth:
total population 64.67 years
male 63.24 years
female 66.17 years (1994 est.)
Total fertility rate:
6.26 children born/woman (1994 est.)
Nationality:
noun Maldivian(s)
adjective Maldivian
Ethnic divisions: Sinhalese, Dravidian, Arab, African
 Religions: Sunni Muslim
Religions: Sunni Muslim
Languages:
Divehi (dialect of Sinhala; script derived from Arabic), English spoken by
most government officials
Literacy: age 15 and over can
read and write (1985)
total population 92%
male 92%
female 92%
Labor force: 66,000 (est.)
by occupation fishing industry 25%
Names:
conventional long form Republic of Maldives
conventional short form Maldives
Digraph: MV
Type: republic
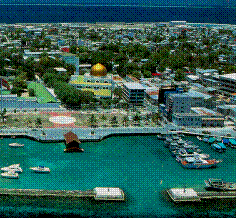 Capital: Male
Capital: Male
Administrative divisions:
19 districts (atolls); Aliff, Baa, Daalu, Faafu, Gaafu Aliff, Gaafu Daalu,
Haa Aliff, Haa Daalu, Kaafu, Laamu, Laviyani, Meemu, Naviyani, Noonu, Raa,
Seenu, Shaviyani, Thaa, Waavu
Independence: 26 July 1965
(from UK)
National holiday: Independence Day, 26 July (1965)
Constitution: 4 June 1968
Legal system:
based on Islamic law with admixtures of English common law primarily
in commercial matters; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction
Suffrage: 21 years of age; universal
Executive branch:
chief of state and head of government President Maumoon Abdul
GAYOOM (since 11 November 1978); election last held 1 October 1993 (next to
be held NA); results - President Maumoon Abdul GAYOOM was reelected with 92.76%
of the vote
cabinet Ministry of Atolls; appointed by the president
Legislative branch: unicameral
Citizens' Council (Majlis)
elections last held on 7 December 1989 (next to be held 7 December 1994);
results - percent of vote NA; seats - (48 total, 40 elected)
Judicial branch: High Court
Political parties and leaders:
no organized political parties; country governed by the Didi clan for
the past eight centuries
Member of: AsDB, C, CP, ESCAP,
FAO, G-77, GATT, IBRD, ICAO, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IMF, IMO, INTELSAT (nonsignatory
user), INTERPOL, IOC, ITU, NAM, OIC, SAARC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU,
WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
Diplomatic representation in US: Maldives
has no embassy in the US, but does have a UN mission in New York; Permanent
Representative to the UN Ahmed ZAKI
consular agency Midhath
Hilmy, Male
telephone 2581
Flag: red with
a large green rectangle in the center bearing a vertical white crescent; the
closed side of the crescent is on the hoist side of the flag
Overview: The economy is based on fishing,
tourism, and shipping. Agriculture is limited to the production of a few subsistence
crops that provide only 10% of food requirements. Fishing is the largest industry,
employing 25% of the work force and accounting for over 60% of exports; it
is also an important source of government revenue. During the 1980s tourism
became one of the most important and highest growth sectors of the economy.
In 1988 industry accounted for about 5% of GDP. Real GDP is officially estimated
to have increased by about 10% annually during the period 1974-90.
National product: GDP - exchange rate conversion - $140 million (1991
est.)
National product real growth rate: 6% (1993 est.)
National product per capita: $620 (1991 est.)
Inflation rate (consumer prices): 15% (1993 est.)
Unemployment rate:
NEGL%
Budget:
revenues $95 million (excluding
foreign transfers)
expenditures $143 million, including capital
expenditures of $71 million (1993 est.)
Exports: $56.3
million (f.o.b., 1993 est.)
commodities fish, clothing
partners US, UK, Sri Lanka
Imports: $173.6 million
(c.i.f., 1993 est.)
commodities consumer goods, intermediate and
capital goods, petroleum products
partners Singapore, Germany,
Sri Lanka, India
External debt: $148 million (1993 est.)
Industrial production: growth rate 24% (1990); accounts
for 6% of GDP
Electricity:
capacity 5,000 kW
production 11 million kWh
consumption per capita 50 kWh (1990)
Industries: fishing and fish processing, tourism, shipping,
boat building, some coconut processing, garments, woven mats, coir (rope),
handicrafts
Agriculture: accounts for almost 25% of GDP
(including fishing); fishing more important than farming; limited production
of coconuts, corn, sweet potatoes; most staple foods must be imported; fish
catch of 67,000 tons (1990 est.)
Economic aid:
recipient US commitments, including Ex-Im (FY70-88), $28 million; Western
(non-US) countries, ODA and OOF bilateral commitments (1970-89), $125 million;
OPEC bilateral aid (1979-89), $14 million
Currency: 1
rufiyaa (Rf) = 100 laari
Exchange rates: rufiyaa (Rf) per
US$1 - 11.105 (January 1994), 10.957 (1993), 10.569 (1992), 10.253 (1991),
9.509 (1990), 9.0408 (1989)
Fiscal year: calendar year
Highways:
total
NA
paved NA
unpaved NA (Male has 9.6 km
of coral highways within the city)
Ports: Male, Gan
Merchant marine: 14 ships (1,000 GRT or over) totaling 38,848 GRT/58,496
DWT, cargo 12, container 1, oil tanker 1
 Airports:
Airports:
total 2
usable 2
with permanent-surface runways
2
with runways over 3,659 m 0
with runways 2,440-3,659 m
2
with runways 1,220-2,439 m 0
Telecommunications:
minimal domestic and international facilities; 2,804 telephones; broadcast
stations - 2 AM, 1 FM, 1 TV; 1 Indian Ocean INTELSAT earth station